What Can Be Inferred When a Professional Is Said to Have Ethical Sensitivity?
- Inquiry
- Open Admission
- Published:
Reliability and validity evaluation of the chinese version of the ethical sensitivity questionnaire for nursing students
BMC Nursing volume 20, Commodity number:244 (2021) Cite this commodity
Abstract
Background
Advances in technology and the expansion of nursing roles have led to complex upstanding bug in nursing. Nursing students are the future clinical nursing workers and practitioners. The ethical sensitivity of nursing students is very important to the professional person evolution of nursing students, which can strengthen the ethical knowledge of nursing students, improve the upstanding decision-making ability of nursing students, and is beneficial to the development of nursing students in the process of clinical practise and nursing instruction. Still, at that place are no instruments to evaluate the ethical sensitivity of nursing students in China. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Chinese version of the Ethical Sensitivity Questionnaire for Nursing Students (ESQ-NS).
Methods
After obtaining the authorization of the author of the original scale, the study used the Brislin dorsum-translation method for translation. An exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and a confirmatory cistron analysis (CFA) were performed to examine the underlying factor structure of the translated questionnaire. The Cronbach blastoff coefficient, the exam-retest reliability, and the corrected detail-total correlation were calculated to verify the internal consistency of the scale.
Results
The Chinese version of ESQ-NS retained 13 items. Exploratory factor analysis (EFA) extracts iv common factors, and the cumulative variance contribution rate is 62.479%. The CFA reached the adaptive standard, and the discriminant validity of the calibration was good. The Cronbach alpha coefficient of this scale was 0.821, and 4 dimensions were between 0.708 and 0.738. The results of the test-retest showed that Pearson'due south correlation coefficient of the overall ESQ-NS was 0.814. Corrected particular-total correlation ranged from 0.337 to 0.542.
Conclusions
The Chinese version of the ESQ-NS has good reliability and validity, which can exist used to evaluate the level of ethical sensitivity of nursing students in China.
Introduction
With the rapid evolution of high and new medical applied science and the electric current social transformation period, there have been some new changes in the nurse-patient relationship [1]. The work of nurses is no longer a unproblematic operation of basic skills such as injection and medicine dispensing, only we need to constantly explore the new changes in the new era of nursing ethics, and then as to guide the cultivation of the professional ethics of nurses, nursing professional person elements and ethical requirements internalized into nurse beliefs habits [2,3,4]. Therefore, information technology is particularly of import to pay attention to the cultivation of ethical sensitivity. Ethical sensitivity is an of import part of nursing practise. No matter the in-office behavior required by the position or the spontaneous out-of-function behavior, they are all in the ethical context of communicating and dealing with patients [five]. The ability to place upstanding issues is a lifelong learning procedure for nursing staff. Ethical sensitivity has been proved to be related to understanding ethical dilemma and dealing with ethical conflict, cultivating clinical ethical decision-making ability, forming upstanding professional accomplishment and practicing upstanding behavior norms [6,7,8].
Ethical sensitivity is a positive attribute in theory, and sensation of the existence of upstanding issues is a prerequisite for decision-making and taking deportment [9]. Improving the ethical sensitivity of nursing students can strengthen the ethical cognition of nursing students and enhance the practice ability of clinical decision-making [10]. In the face up of the new pattern of health development, nursing students must go on up with the trend and constantly better their ain ethical sensitivity. Loftier ethical sensitivity is conducive to improving the ability of combining nursing students' professional level with nursing ethics and moral quality. Lack of upstanding sensitivity volition lead to the loss of moral responsibility and negative health consequences.
Upstanding sensitivity is an evolving concept. Rest [eleven] defined ethical sensitivity as the ability to make ethical decisions without obvious ethical conflicts and to evaluate the reactions and feelings of others and to recognize their relative importance to the patient and the potential course of action to have. Lützén and colleagues [12] pointed out that ethical sensitivity is the ability to testify contextual and intuitive understanding of patients' vulnerable situations, to recognize upstanding conflicts and to have insight into the ethical consequences of their decisions.
Previous studies have shown that the Moral Sensitivity Questionnaire (MSQ) adult by Lützén and colleagues [12] was often used to measure ethical sensitivity among nurses in Japan [thirteen] and Korea [14]. Even so, China lacks such instruments. Although some studies have besides used the Moral Sensitivity Questionnaire-Revised Version into Chinese (MSQ-R-CV) translated by Huang et al. in 2015 [xv], which is mainly used by nurses or professionals. Currently, at that place is a lack of effective tools to assess the level of ethical sensitivity of nursing students. This must be urgently addressed and then that the pedagogy and grooming sector can be kept informed.
Taeko Muramatsu and colleagues [xvi] defined the ethical sensitivity of nursing students every bit the ability to identify ethical issues in nursing practice and developed a validated instrument called the Ethical Sensitivity Questionnaire for Nursing Students (ESQ-NS). Altogether, 13 items for nursing students were identified and classified into there domains: respect for individuals, distributive justice, and maintaining patients' confidentiality. Studies [17,xviii,19] have shown that upstanding sensitivity can be improved through training and educational activity. The measuring instrument of ethical sensitivity can aid nursing students understand their sensitivity level more conspicuously, which is conducive to making upward for their shortcomings. Information technology can promote nursing students in the future nursing practice can be sensitive to find the patient's bug, understand the patient'southward situation, as far as possible to avoid the occurrence of nurse-patient conflict. In a complex and challenging health care environment, this is critical for the future development of nursing students. The purpose of this report was to translate ESQ-NS into Chinese and to describe the reliability and validity of the Chinese version of ESQ-NS amongst nursing students.
Methods
Written report design and participants
A cross-sectional survey was conducted from Baronial to November 2020 in Liaoning Province, China. Participants included first-year to 4th-year nursing students from Shenyang (Cathay Medical University, Liaoning Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang Medical College) and Jinzhou (Jinzhou Medical University). The research procedures complied with the ethical standards of the institutional inquiry committee, as well as the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments. All participants were given detailed information about the purpose and methodology of the study. We will ensure the information security of everyone, and have signed informed consent before preparing the questionnaire.
Instruments
Upstanding Sensitivity Questionnaire for Nursing Students (ESQ-NS)
Ethical Sensitivity Questionnaire for Nursing Students developed by Taeko Muramatsu and colleagues [16] consists of thirteen items, covering three dimensions: respect for individuals (8 items), distributive justice (3 items), and maintaining patients' confidentiality ( two items). The respondent is asked to rate each item on a 4-point Likert calibration ranging from ane for "strongly disagree" to iv for "strongly concord". The ESQ-NS score ranges from xiii to 52, with college score indicating higher ethical sensitivity. The Cronbach alpha coefficient of this scale was 0.821.
The Chinese Moral Sensitivity Questionaire-Revised Version (MSQ-R-CV)
The Chinese Moral Sensitivity Questionaire-Revised Version (MSQ-R-CV) was translated into Chinese by Huang [15] after strict cultural adjustment. The scale consists of 9 items and contains ii dimensions: moral responsibility and strength (5 items), sense of moral burden (four items). The respondent is asked to rate each detail on a half dozen-bespeak Likert scale ranging from 1 for "strongly disagree" to 6 for "strongly agree". The MSQ-R-CV score ranges from 9 to 54, with higher score indicating higher moral sensitivity. The Cronbach blastoff coefficient of the MSQ-R-CV was 0.82. The MSQ-R-CV was used to measure concurrent validity.
Demographic characteristic
Demographic measures included age, sex, school year, clinical feel, ethical education, and nursing professional attitude.
Procedures
Translation procedure
The original questionnaire was translated into Chinese past two nursing experts respectively, and and then dorsum-translated into English by two English experts co-ordinate to the Brislin translation method [20]. The original questionnaire, the kickoff draft of the Chinese version and the translated English questionnaire were discussed, compared and revised past a psychology expert and a nursing expert who is familiar with Chinese and Western cultural, so equally to make the contents of the questionnaire more consistent with Chinese cultural habits. Finally, we randomly elected x students to assess the revised scale. Based on their feedback, the scale was revised and improved.
Data collection procedure
The students were told that the purpose and significance of the study. Before the beginning of the offline survey, the investigators were uniformly trained, and the investigators explained each detail earlier the students filled in the questionnaire, so as to ensure that each pupil had no doubt about the contents of the questionnaire. After the recollect, the questionnaires were numbered one past one, and the double-entry principle was implemented to ensure the accurateness of the data. A total of 1465 nursing students participated in the study, and 1446 questionnaires (98.70%) were completed for analysis.
Statistical analysis
Data analysis used SPSS 25.0 and AMOS 23.0 (IBM Corporation). Continuous data were expressed as mean (SD) and categorical data as percentages. Calculated the skewness and kurtosis of each detail. When the value is betwixt -2 and +2, the information is considered to be usually distributed [21]. Content validity, structure validity, discriminant validity, concurrent validity, internal consistency, retest reliability and the corrected particular-total correlation of the ESQ-NS calibration were measured in our study.
Content validity
Content validity refers to the appropriateness and consistency between the actual measured content and the content to be measured [22]. Seven experts were invited to evaluate the content validity of the Chinese version of ESQ-NS. Each item is scored on a four-bespeak scale from 1 to iv. The scores indicated no relevance, low relevance, stiff relevance and very strong relevance. Content validity was calculated according to experts scores, including particular-level content validity index (I-CVI) and average scale-level content validity index (South-CVI/Ave).
Structure validity
Structure validity is an indicator to measure whether the tool scores fully reflects the dimension structure [23]. To explore the underlying gene structure of the translated questionnaire, an exploratory cistron assay (EFA) and a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) were performed. The sample of 1446 cases was randomly divided into two groups, i (n=747) for EFA and the other (n=699) for CFA. EFA was used to make up one's mind the structural validity of the Chinese version of the scale. Calculated value of the Bartlett test [24] of sphericity was significant (P<0.05) and the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) [25] was >0.60, indicating that it was suitable for cistron analysis. Master component analysis and varimax rotation method were used to excerpt common factors with eigenvalues greater than 1. Based on the factor division obtained by exploratory gene analysis, AMOS (IBM Corporation) is used to construct the CFA model, analyzing the fit of models and its parameter estimates.
Discriminant validity
The purpose of discriminant validity is to judge whether there is a good discriminant degree between different latent variables [26]. The discriminant validity of the Chinese version of ESO-NS was analyzed by using a 2-tailed independent samples t test. The total score of the ESQ-NS calibration was ranked from depression to high; the bottom 27% of the scores were grouped into the low-score group, and the top 27% of the scores were grouped into the high-score group.
Concurrent validity
Concurrent validity is a kind of criterion validity, which refers to the use of recognized valid scales as standards to test the correlation between the new scale and the standard calibration [27]. Pearson correlation coefficient between ESQ-NS and Chinese version of MSQ-R-CV was used to analyze the concurrent validity. It is generally believed that the concurrent validity is betwixt 0.four and 0.eight [28].
Reliability analysis
The internal consistency of the scale was tested by calculating the Cronbach blastoff coefficient and the corrected particular-total correlation. The time stability of the calibration was evaluated by retest reliability. Afterward an interval of 14 days, 30 nursing students were randomly selected to consummate the scale. In this study, the retest interval of the calibration'southward retest reliability was two weeks. The reason was based on the principle that nursing students basically forget the survey content and are not affected by other environmental factors [29]. It was generally accepted that Cronbach blastoff coefficient and retest reliability greater than 0.70 were acceptable [xxx]. Using 0.3 every bit the inclusion criterion to judge the corrected item-total correlation [31].
Results
Descriptive statistics
The study included 1446 nursing students. The mean age of the participants was 21.three±1.9 years. Nursing students who were female (90.9%), 2nd grade (37.1%) count the most, non-clinical experience(52.viii%), and had ideals education(82.5%), liked the nursing profession(43.0%). Other characteristics are presented in Table i. The mean (SD) score of each item of the Chinese ESQ-NS is shown in Tabular array ii. These data were unremarkably distributed according to the skewness and kurtosis figures.
Validity analysis
Content validity
The content validity of Chinese version of ESQ-NS was evaluated by expert evaluation method [32]. The adept grouping consists of 7 experts, including 3 nursing ethics experts, ii nursing pedagogy experts and 2 nursing experts who are proficient in Chinese and English. The results of content validity analysis showed that I-CVI of ESQ-NS is 0.857~11.000, and the S-CVI / Ave is 0.956.
Explorary factor analysis
The Bartlett examination [24] of sphericity was meaning (χ2 78=2551.037; P<0.001), and the KMO alphabetize [25] was 0.829, greater than the minimum acceptable value of 0.6, which confirmed the feasibility of factor analysis. Principal component analysis and varimax rotation extracted four mutual factors and explained 62.479% of the variance. Tabular array 3 showed the cistron loading for each item. According to the previous research, a cistron loading of 0.4 was selected every bit the cut-off indicate to retain the items [33]. The scree plot further confirmed the four-factor structure, and the descending tendency became weak after the 4th betoken, indicating that it was appropriate to select 4 common factors. After varimax rotation, the four factors explained 17.339%, 16.683%, fifteen.685% and 12.772%, respectively. Figure ane shows the scree plot.
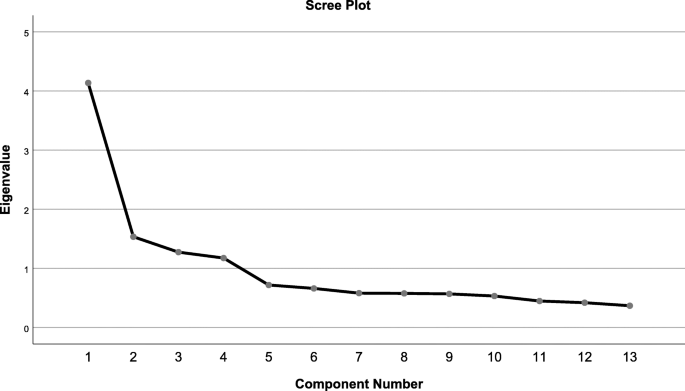
Scree plot of exploratory cistron analysis for Chinese version of the ESQ-NS
Confirmatory factor analysis
Confirmatory cistron analysis was performed on 699 nursing students using a four-cistron model. The present model provides an acceptable fit to the data. Fit indexes are as follows: CMIN/DF (chi-square/degree of freedom)=ii.712, CFI (comparative fit index)=0.959, GFI(goodness of fitness alphabetize)=0.966, AGFI (adjusted goodness of fit index)=0.946, PGFI (parsimonious goodness of fit index) =0.605, IFI (incremental fit index)=0.959, TLI (Tucker Lewis index)=0.944, RMSEA (root mean foursquare fault of approximation)=0.050, and RMR (root mean residual)=0.030. The results of CFA are shown in results are shown in Fig. two.
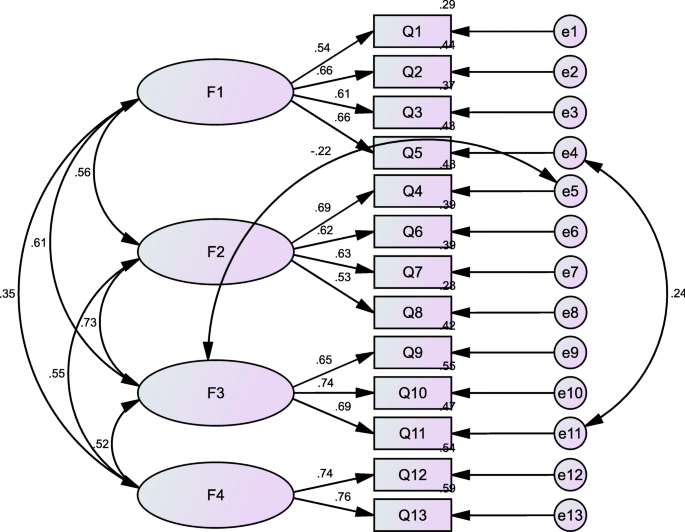
Standardized four-gene structural model of the ESQ-NS (n=699). F1 (Respect for individuals, 4 items), F2 (Reasonable care, four items), F3 (Distributive justice, three items), F4 (Maintaining patients' confidentiality, two items).
Discriminant validity
In this study, extreme grouping method was used to analyze the discriminant validity. The total scores were ranked from high to low, and the critical value was 27%. The scores≥39 were classified as high group, and≤33 were classified as depression group. The results showed that the scores of each item had statistical significance in both high and low areas (P < 0.05). This indicates that each item of ESQ-NS has a skilful degree of bigotry, and the discrimination power of each particular of the scale is good. The results are shown in Tabular array four.
Concurrent validity
The Pearson correlation between ESQ-NS full score and MSQ-R-CV total score was 0.488, indicating a skillful correlation. This means that the measurement tool can effectively measure the characteristics of the concept to be measured.
Reliability analysis
The results of reliable analysis testify that ESQ-NS had ideal internal consistency. The internal consistency of alpha was 0.821, and the four dimensions of Cronbach alpha coefficient were 0.714, 0.708, 0.738 and 0.710, respectively. Table 5 shows the change of Cronbach alpha value after the exclusion of a item item from the questionnaire. The corrected item-total correlation of the items ranged from 0.337 to 0.542, all greater than 0.iii. 2 weeks later, 30 nursing students were randomly selected to evaluate the reliability of the scale retest. The retest reliability was 0.814.
Give-and-take
The Chinese version of ESQ-NS calibration strictly followed the procedures of translation, back-translation, cultural adjustment and pre-survey [20]. At each stage, the experts discussed and modified fully, and co-ordinate to the Chinese guidelines and common expressions, the Chinese version of ESQ-NS was obtained.
The results of this study showed that the items of the Chinese version of ESQ-NS were consistent with those of the original scale, and no items were deleted. However, the factor structure of the Chinese version is slightly different from that of the original ane. The original ESQ-NS had three dimensions: respect for individuals (Item ane-viii), distributive justice (Item nine-11) and maintaining patients' confidentiality (Item 12-13), with a total of 13 items. In this study, exploratory factor analysis showed that the start cistron had four items, involving the original scale one, 2, 3 and 5, named "respect for individuals". Factor ii had 4 items in total, involving the original scale four, 6, 7 and 8. Based on expert opinions, literature review and the underlying characteristics of the items, we renamed it "reasonable care". The dimensions of factor 3 and cistron 4 were exactly the aforementioned as those of the original scale, indicating that they were easier to apply cross-culturally. An EFA determined 13 items categorized under iv factors (respect for individuals, reasonable care, distributive justice, maintaining patients' confidentiality), which explained 62.479% of the full variance. Each item had a cistron loading of 0.threescore or higher, which was considered platonic [34].
The researchers interpreted and labeled the emerging factor according to the core concepts of the human intendance theory by WATSON J [35]. The 2nd factor ("reasonable care") explains 16.683% of the full variance and should exist considered as the main attribute for the existence of a valid assessment of ESQ-NS level. Watson'south theory points out that intendance is the essence of nursing, which provides theoretical core knowledge for patient care and provides a new dimension for revealing the core essence of nursing. Literature [36, 37] take revealed that in the analysis and application of human care theory, the dynamic change of human being intendance needs in different stages plays an important role in clinical nursing do, nursing education, nursing direction and other fields. In fact, studies [38, 39] have shown that due to the lack of safe nursing knowledge and medication methods. Many patients have been admitted to professional institutions for handling or formal care, which also suggests that nursing staff should strengthen the study of bones principles and ethical requirements of care. Nursing students are the reserve forcefulness of medical service application-oriented talents. Their willingness to intendance direct affects the quality of future care system professionals [twoscore]. Therefore, we use "reasonable care" as an independent factor in evaluating ethical sensitivity tool, rather than being included among other factors.
In our study, in improver to the 3 bones aspects of the original version, our scale includes "reasonable intendance" (factor two), which makes the domain classification of the Chinese scale more specific. Considering that the incidence of nurse-patient relationship, nurse-patient disputes, nurse-patient conflicts and other cases is increasing year by twelvemonth, nursing students believe that the focus of professional person nursing is to intendance patients, hope to accept amend care of patients through their own ability, and take a stronger sense of responsibility for taking intendance of patients [41]. This may be influenced by unlike medical environment, cultural background and subject education at home and away. Different regions have different educational modes for nursing students, so they have different understandings of problems. Further research is needed to run into if the findings can be applied to other cultures.
Co-ordinate to the expert evaluation method, the content validity range of I-CVI of each particular level was 0.857~one.000 ( I-CVI≥0.78) [22]. The value of I-CVI ranges from 0 to 1. A larger value indicates that the particular is more representative and more suitable for the items in the calibration. The S-CVI/Ave of ESQ-NS reached 0.956 (>0.xc), indicating that the scale has practiced content validity [42]. The analysis shows that the Bartlett spherical examination<0.01, KMO>0.6, with a value of 0.857 indicating a moderate-to-loftier level of capability of the correlation matrix, which shows that the data are suitable for factor analysis. Four mutual factors were obtained through CFA analysis, each alphabetize has good adaptability and within a reasonable range (CMIN/DF<three, CFI, IFI, GFI, AGFI,TLI>0.90,PGFI>0.50,RMR<0.05, RMSEA<0.08). The results testify that cistron loading and interpretation variance are strong, which are consequent with EFA results, and have a practiced four-factor construction and model fitting alphabetize. The findings showed that the Chinese version of ESQ-NS could reflect the ethical level of nursing students and the role of nursing students in 4 dimensions. A significant positive correlation was found between ESQ-NS and MSQ-R-CV (r=0.488, P<0.001). The results show that the concurrent validity was well.
In the ESQ-NS, the internal consistency of the Chinese version of ESQ-NS and its 4 dimensions, every bit measured by Cronbach blastoff coefficient, were all greater than 0.7. The internal consistency were consistent with those of the original study [16]. Corrected item-total correlation are greater than 0.3. Test-retest reliability of the whole scale was 0.814. All result show that the calibration is stable and all indexes are inside a reasonable range, so it can exist considered every bit a reliable cess tool to be applied to Chinese nursing students.
Limitations
This study has shortcomings. The participants of this study were only higher students from Liaoning Province, and female participants were significantly higher than male person participants. Therefore, these findings do non correspond wishes of all nursing students in China. Attention should be paid to the ratio of gender of samples, expand the coverage of samples, and farther evaluate the adaptability of the scale of ethical sensitivity of nursing students in the whole country.
Conclusions
Ethical sensitivity is a key gene in the ethical education and nursing do of nursing students. An increasing number of health care researchers pay attention to it. Effective and feasible assessment tools for upstanding sensitivity are essential for nursing educators and nursing students. The Chinese version of the instrument, which supports a iv-cistron structure, proved to be reliable. In future research, nosotros believe that it is necessary to employ the ESQ-NS at the end of every academic year'south theoretical and practical courses to appraise upstanding sensitivity of nursing students, so as to provide an empirical ground for finer improving nursing students' ethical decision-making power and preventing ethical dilemmas.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the electric current written report are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
-
Albert JS, Younas A, Sana S. Nursing students' upstanding dilemmas regarding patient care:An integrative review. Nurse Educ Today.2020;88:104389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2020.104389
-
Hegenbarth M, Rawe S, Murray 50, Arnaert A, Chambers-Evans J. Establishing and maintaining the clinical learning environment for nursing students: a qualitative study. Nurse Educ Today. 2015;35(2):304–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2014.ten.002
-
Eckardt M, Lindfelt One thousand. An analysis of nursing students' ethical conflicts in a hospital. Nurs Ethics. 2019;26(seven-8):2413–2426. https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733018784730
-
Hemberg J, Hemberg H. Ethical competence in a profession: Healthcare professionals' views. Nurs Open. 2020;7(four):1249–1259. https://doi.org/10.1002/nop2.501
-
Guo B, Zhao 50, Gao Y, Peng 10, Zhu Y. The status of professional person identity and professional self-efficacy of nursing students in Cathay and how the medical documentaries affect them: A quasi-randomized controlled trial. Int J Nurs Sci. 2017;4(ii):152–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2017.03.006
-
Mehdipour Rabori R, Dehghan M, Nematollahi M. Nursing students' upstanding challenges in the clinical settings: A mixed-methods written report. Nurs Ethics. 2019;26(seven-8):1983-1991. https://doi.org/ten.1177/0969733018810766
-
Bremer A, Holmberg Thou. Ethical conflicts in patient relationships: Experiences of ambulance nursing students. Nurs Ethics. 2020;27(4):946–959. https://doi.org/ten.1177/0969733020911077
-
Sari D, Baysal E, Celik GG, Eser I. Ethical Determination Making Levels of Nursing Students. Pak J Med Sci. 2018;34(3):724–729.https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.343.14922
-
Esmaelzadeh F, Abbaszadeh A, Borhani F, Peyrovi H. Ethical Sensitivity in Nursing Ethical Leadership: A Content Analysis of Iranian Nurses Experiences. Open Nurs J. 2017;11:one–13. Published 2017 January 31. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874434601711010001
-
Ghasemi Southward, Ahmadi F, Kazemnejad A. Responsibleness among bachelor degree nursing students: A concept analysis. Nurs Ethics. 2019;26(5):1398–1409. https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733018754369
-
Residual JR. Development in judging moral issues. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press; 1979.
-
Lützén 1000, Nordström G, Evertzon One thousand. Moral sensitivity in nursing practice. Scand J Caring Sci. 1995;9(3):131–138. https://doi.org/x.1111/j.1471-6712.1995.tb00403.ten
-
Maeda J, Konishi E. Evolution and validation of a Japanese version of the revised moral sensitivity questionnaire: a preliminary written report. J Jpn Nurs Ethics. 2012;four(1):32–7 in Japanese
-
Han SS, Kim J, Kim YS, Ahn South. Validation of a Korean version of the Moral Sensitivity Questionnaire. Nurs Ethics. 2010;17(ane):99–105. https://doi.org/x.1177/0969733009349993
-
Huang FF, Yang Q, Zhang J, Zhang QH, Khoshnood M, Zhang JP. Cross-cultural validation of the moral sensitivity questionnaire-revised Chinese version. Nurs Ideals. 2016;23(7):784–793. https://doi.org/ten.1177/0969733015583183
-
Muramatsu T, Nakamura Thousand, Okada Due east, Katayama H, Ojima T. The evolution and validation of the Upstanding Sensitivity Questionnaire for Nursing Students. BMC Med Educ. 2019;xix(1):215. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1625-8
-
Palazoğlu CA, Koç Z. Upstanding sensitivity, burnout, and job satisfaction in emergency nurses. Nurs Ethics. 2019;26(iii):809–822https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733017720846
-
Basar Z, Cilingir D. Evaluating ethical sensitivity in surgical intensive care nurses. Nurs Ethics. 2019;26(7-8):2384–2397. https://doi.org/x.1177/0969733018792739
-
Yuguero O, Esquerda M, Viñas J, Soler-Gonzalez J, Pifarré J. Ethics and empathy: The relationship between moral reasoning, ethical sensitivity and empathy in medical students. Rev Clin Esp (Barc). 2019;219(2):73–78https://doi.org/x.1016/j.rce.2018.09.002
-
Brislin RW. Back-translation for cross‐cultural inquiry. J Cross Cult Psychol. 1970;1:185‐216.
-
Adawi Grand, Bragazzi NL, Argumosa-Villar L, et al. Translation and Validation of the Nomophobia Questionnaire in the Italian Linguistic communication: Exploratory Factor Analysis. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018;6(1):e24.https://doi.org/ten.2196/mhealth.9186
-
Lynn MR. Determination and quantification of content validity. Nurs Res.1986;35(half-dozen):382–385.
-
Mokkink LB, Terwee CB, Patrick DL, Alonso J, Stratford PW, Knol DL, et al. The COSMIN study reached international consensus on taxonomy, terminology, and definitionsof measurement properties for health-related patient-reported outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol. 2010;63(7):737–45.https://doi.org/ten.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.02.006.
-
Bartlett MS. A notation on the multiplying factors for various χ2 approximations. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol 1954;sixteen:296–298.
-
Kaiser HF. An index of factorial simplicity. Psychometrika 1974;39:31–36.
-
Gao Y, Dai H, Jia Chiliad, et al. Translation of the Chinese Version of the Nomophobia Questionnaire and Its Validation Amid College Students: Factor Analysis. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020;8(3):e13561.https://doi.org/10.2196/13561
-
Shen WQ, Chen HL, Hu Y. The validity and reliability of the self-directed learning musical instrument (SDLI) in mainland Chinese nursing students. BMC Med Educ. 2014;xiv:108.https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-xiv-108.
-
Fang JQ. Medical statistics and computer experiments [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific discipline and Technology Press,2001.
-
Terwee CB, Bot SD, de Boer MR, et al. Quality criteria were proposed for measurement properties of health condition questionnaires. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60(1):34–42.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.03.012.
-
Cronbach LJ. Research on classrooms and schools: Formulation of questions, design and analysis: Stanford evaluation consortium: Stanford University; 1976
-
Ferketich S. Focus on psychometrics. Aspects of item analysis. Res Nurs Wellness. 1991;14(two):165–168. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.4770140211
-
Hambleton RK, Swaminathan H. Criterion-referenced testing and meas-urement: a review of technical issues and developments. Rev Educ Res. 1978;48(1):i–47.
-
Boone KB, Pontón MO, Gorsuch RL, González JJ, Miller BL. Factor analysis of 4 measures of prefrontal lobe functioning. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 1998;xiii(7):585–595.
-
Hu Y, Tiew LH, Li F. Psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the spiritual care-giving scale (C-SCGS) in nursing do. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-019-0662-vii
-
Watson J. Nursing: homo science and man intendance. A theory of nursing. NLN Publ. 1988;(fifteen-2236):1–104.
-
Durgun Ozan Y, Okumuş H. Furnishings of Nursing Intendance Based on Watson's Theory of Human Caring on Anxiety, Distress, And Coping, When Infertility Treatment Fails: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Caring Sci. 2017;half-dozen(2):95–109. https://doi.org/10.15171/jcs.2017.010
-
Pajnkihar One thousand, McKenna HP, Štiglic G, Vrbnjak D. Fit for Practice: Analysis and Evaluation of Watson'due south Theory of Human being Caring. Nurs Sci Q. 2017;30(3):243–252. https://doi.org/10.1177/0894318417708409
-
Jorge C, Cetó Grand, Arias A, et al. Level of understanding of Alzheimer affliction among caregivers and the full general population. Nivel de conocimiento de la enfermedad de Alzheimer en cuidadores y población full general. Neurologia. 2021;36(6):426–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nrl.2018.03.004
-
Kang 50, Liu XH, Zhang J, et al. Attitudes Toward Advance Directives Among Patien and Their Family unit Members in Communist china. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017;xviii(ix):808.ehttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2017.05.014
-
Chi MJ, Shyu ML, Wang SY, Chuang HC, Chuang YH. Nursing Students' Willingness to Care for Older Adults in Taiwan. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2016;48(ii):172–178. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnu.12197
-
Guo 50, Jones MC, Liu Y, Yv S, Zhu Y, Guo Y. Cantankerous-cultural validation of the Pupil Nurse Stress Alphabetize Calibration: A descriptive survey targeting student nurses in China. JAffect Disord. 2019;251:31–38https://doi.org/x.1016/j.jad.2019.03.017
-
Shrout PE, Fleiss JL. Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull. 1979;86(two):420–428. https://doi.org/10.1037//0033-2909.86.two.420.
Acknowledgements
We thank the 4 universities who supported our data drove and all the participants and nosotros would similar to thank Professor Taeko Muramatsu for providing the ESQ-NS scale.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 201602297).
Author information
Affiliations
Contributions
HY, TT and CL conceived and designed the study. HY, CL, HZ, and HT helped with data collection. HY, TT, YG and HT provided statistical advice on report design and performed data analysis. HY, TT, YG contributed to manuscript training and revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ideals approval and consent to participate
All procedures were carried out in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki proclamation, and the inquiry proposal was canonical by the Ethics Committee of Jinzhou Medical University (JZMULL2021009). All study participants received informed consent.
Consent for publication
Non applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they take no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed nether a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in whatever medium or format, as long every bit you give appropriate credit to the original author(southward) and the source, provide a link to the Artistic Commons licence, and bespeak if changes were made. The images or other third party cloth in this article are included in the commodity's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the textile. If textile is non included in the article'south Creative Eatables licence and your intended use is not permitted past statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you volition need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Artistic Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/nothing/1.0/) applies to the information fabricated available in this commodity, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and Permissions
Well-nigh this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Tong, T., Gao, Y. et al. Reliability and validity evaluation of the chinese version of the ethical sensitivity questionnaire for nursing students. BMC Nurs 20, 244 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-021-00768-z
-
Received:
-
Accepted:
-
Published:
-
DOI : https://doi.org/ten.1186/s12912-021-00768-z
Keywords
- Ethical sensitivity
- Nursing students
- Validity
- Reliability
Source: https://bmcnurs.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12912-021-00768-z
0 Response to "What Can Be Inferred When a Professional Is Said to Have Ethical Sensitivity?"
Post a Comment